9 Installing Python and the opensafely command line interface
- Environment variables in computer operating systems contain important strings of text
- The
PATHenvironment variable is a list of folders which the computer searches in when you type the name of an executable into the command line shell program (usuallyzshon macOS,bashon Ubuntu,cmdorPowershellon Windows) - To use the
python/python3andpip/pip3commands at the shell command line we need to install Python and make sure the folder containing its executable is in ourPATHenvironment variable (unless you already know all of this and are going to run Python in Anaconda through the Anaconda Prompt)
9.1 macOS
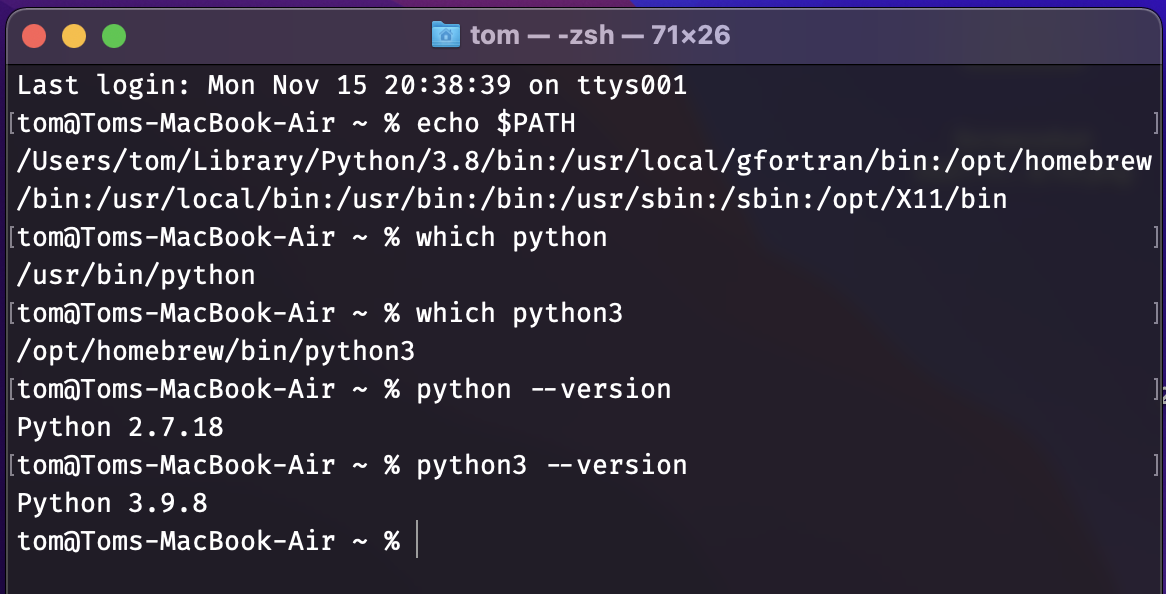
If you have a Mac, the macOS operating system comes with an old-ish version of Python 2.7
I recommend installing Python 3 through homebrew
brew install pythonWhen you open Terminal
See the contents of
PATHwithecho $PATH(note use${PATH}in shell scripts)you should be able to find the
python/python3exectables with thewhichcommand
9.2 Windows
You have a number of choices where to install Python from
Despite not being recommend - it is better for you to add Anaconda/Python to your
PATHin the installer options, i.e., check the first box on this screen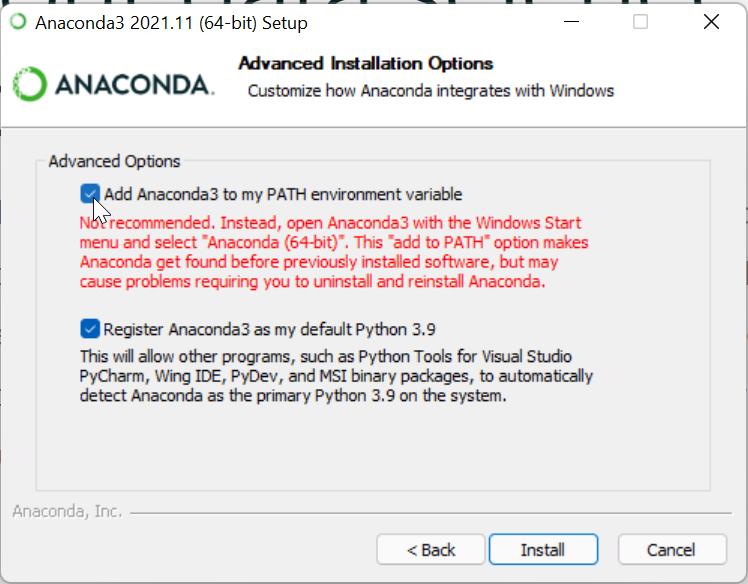
And in the Python installer check the box adding Python to
PATH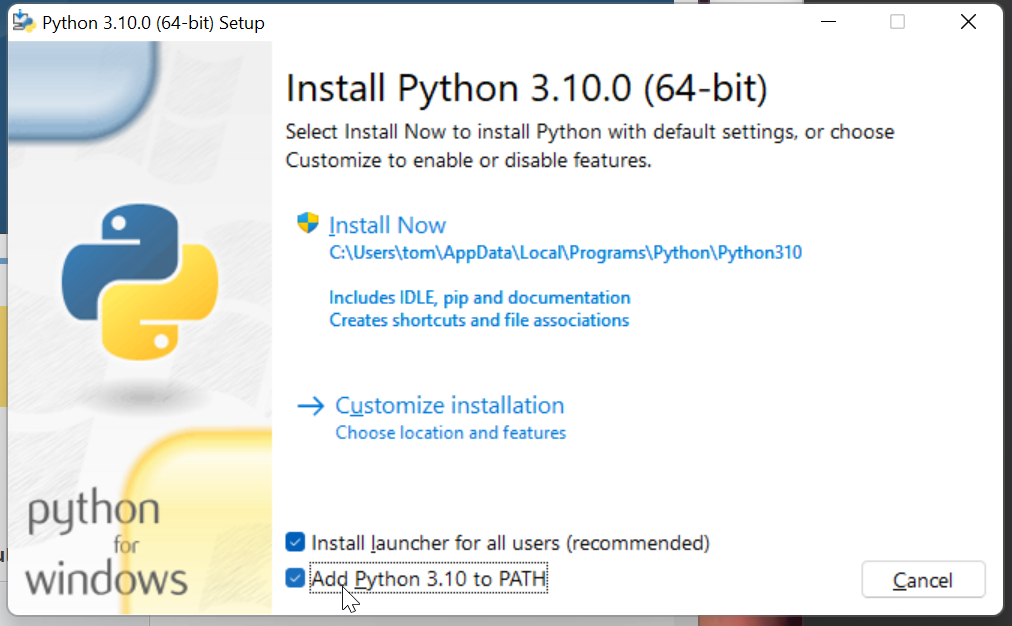
Open Windows Terminal
you can see the contents of
PATHin Powershell with$Env:Path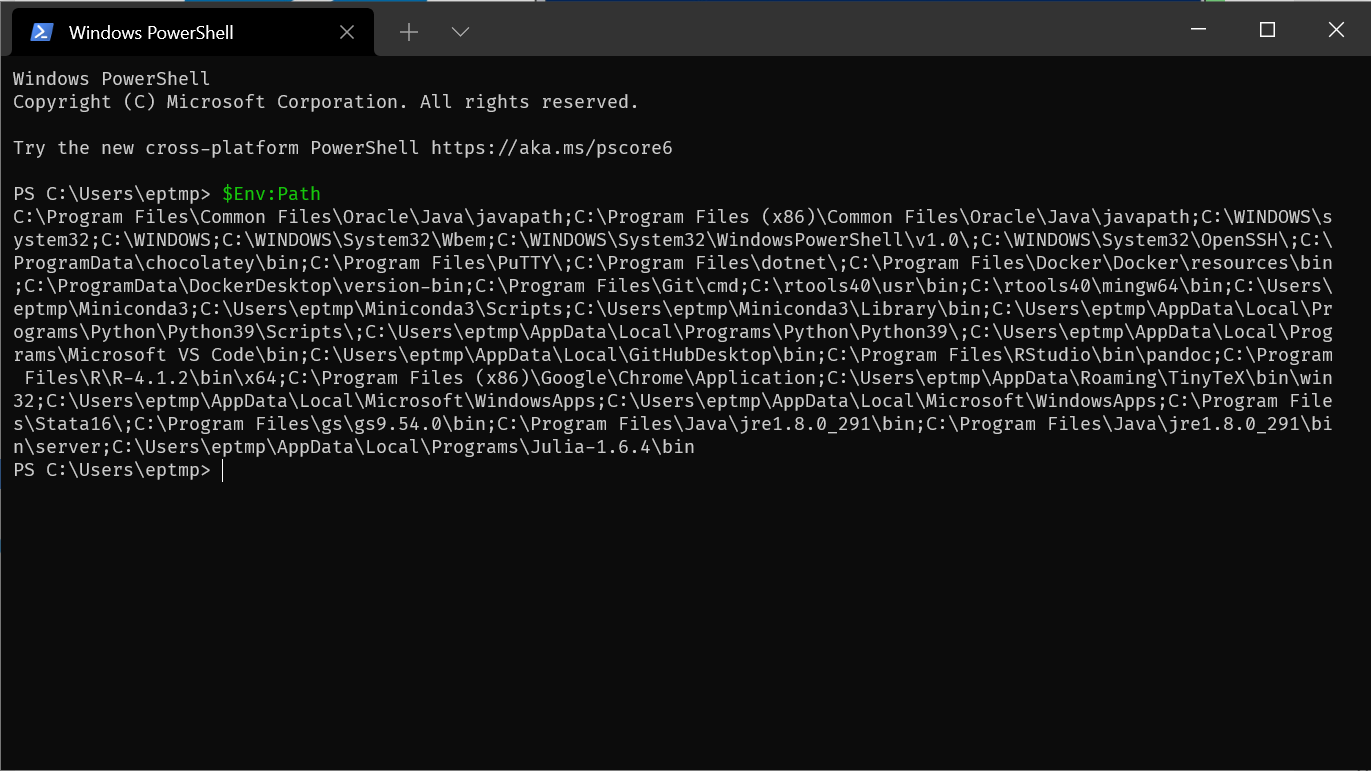
and in
cmdwithecho %PATH%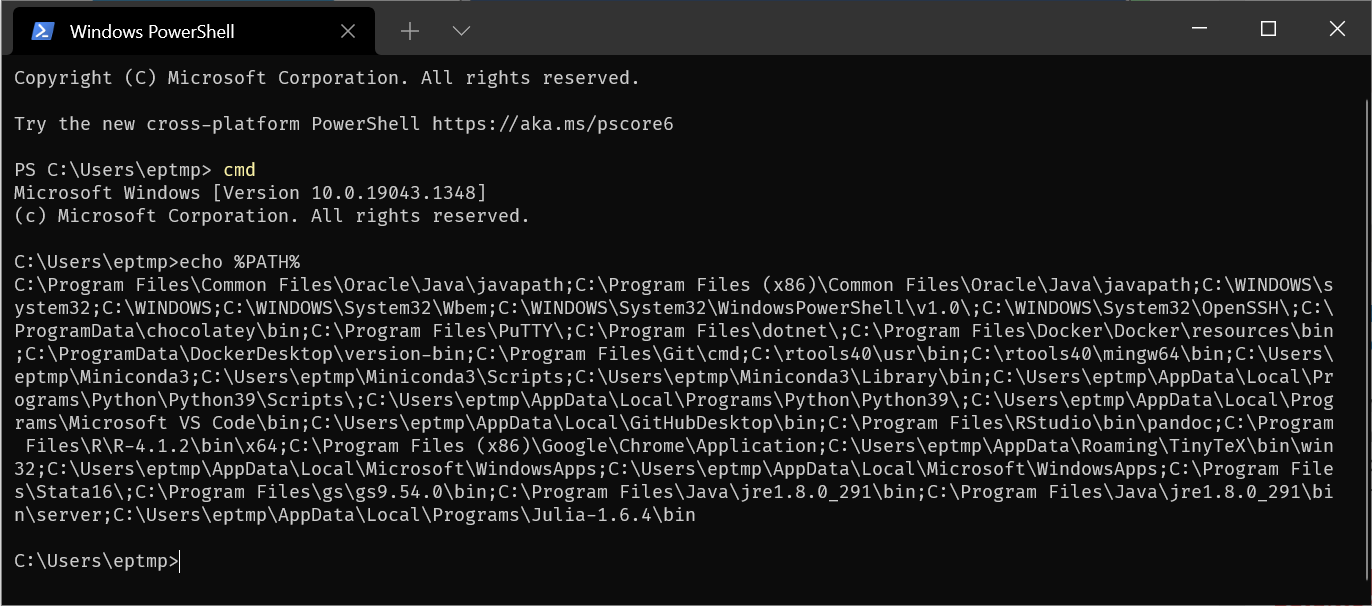
you can see the location of the Python executable in
cmdwithwhere python/where python3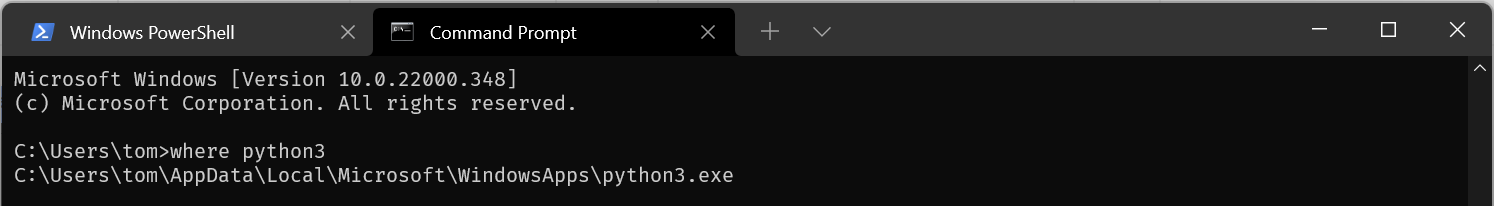
If you installed Anaconda and you did not add its folders to
PATHthen you need to install and run opensafely using the Anaconda prompt - you find this as a program under the Start menu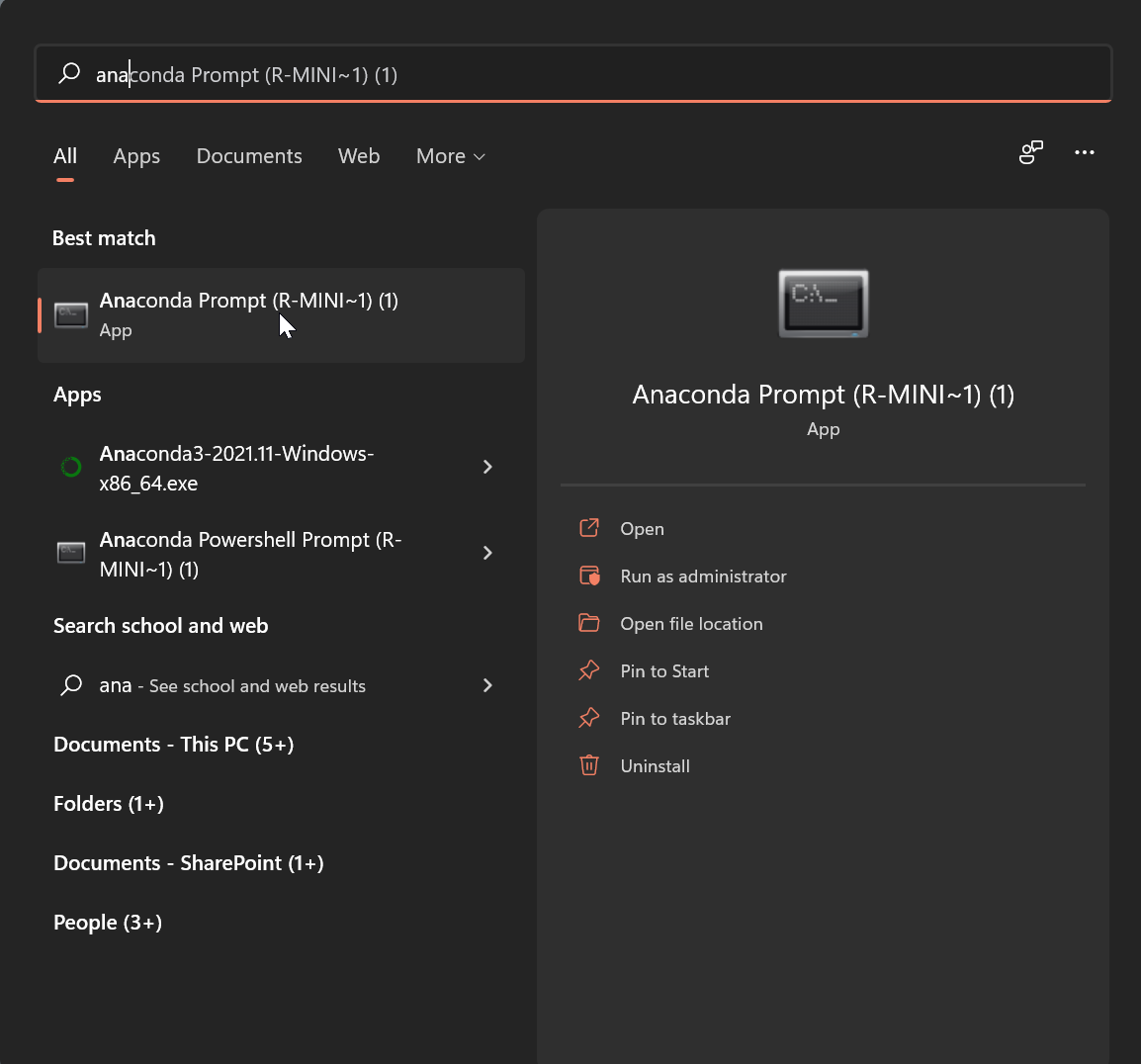
9.3 Installing the opensafely package
As long as the
python/python3andpip/pip3executables are now on yourPATHyou can simply run in your shell programpip install opensafelyThis will additionally install its dependency package the cohortextractor package into your Python installation and you should now be able to run opensafely commands such as
opensafely run run_all