7 Git and GitHub
- Use a visual Git editor, e.g. GitHub Desktop
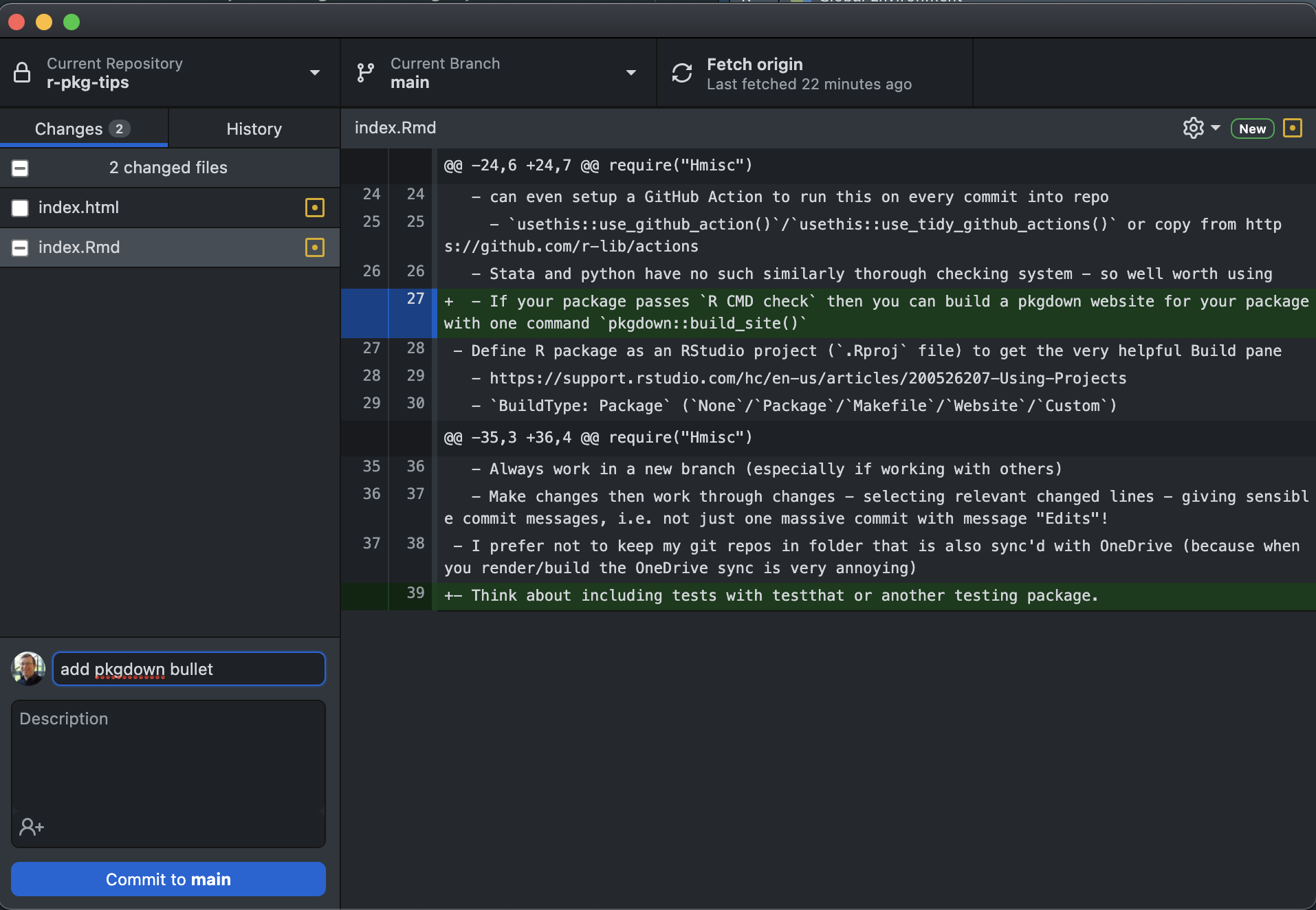
- Work in a new branch, especially if working with others
- Then merge into main/master when you’re sure your changes are what you want
- When coding, I recommend making your changes
Then select relevant changed lines
Use sensible commit messages, i.e., do not make one massive commit with commit message “Edits”!
- I prefer not to keep my Git repositories in a folder which is also synchronized with OneDrive/Google Drive, e.g., when you render an R Markdown file the syncing of all the auxiliary files that are created can be very annoying
- When contributing to a new package, after forking on GitHub, then cloning to your local machine, and opening in RStudio/setting working directory to top level of package run
devtools::install_dev_deps()to install all packages under Depends, Imports, and Suggests in itsDESCRIPTIONfile - Your repo can contain much more than just your R package
- It will often additionally contain the static website for the package (made with pkgdown) which can be hosted for free using GitHub Pages/Netlify
- Remember to exclude the files/folders not the package by adding them to the
.Rbuildignorefile
- Some people don’t like others distributing packages through a GitHub repo, because
install_github()looks for a change in the hash of the latest commit - but that may have been in a file not included in the source package